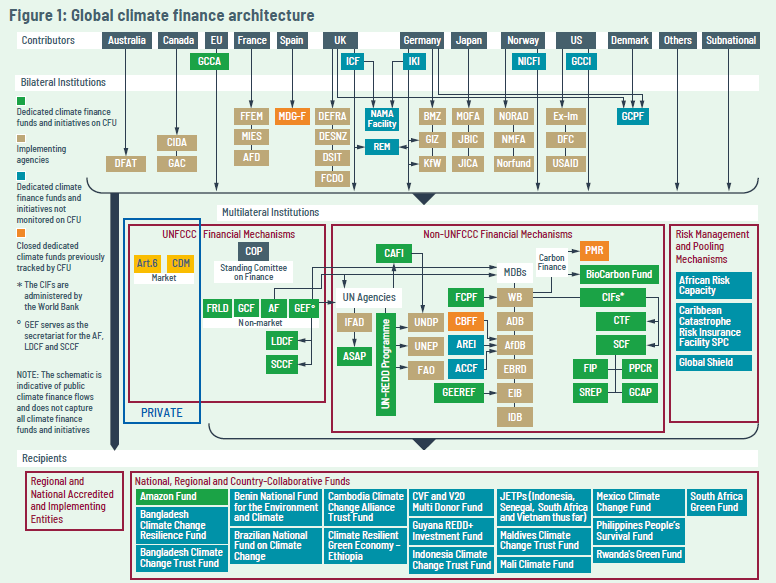
The global climate finance architecture is complex and always evolving. Funds flow through multilateral channels – both within and outside the UNFCCC Financial Mechanism – as well as through bilateral and regional initiatives and channels. A growing number of recipient countries are also setting up national climate change funds that receive funding from multiple contributor countries in an effort to coordinate and align contributor interests with national priorities.
This figure provides an overview of the global architecture, focusing particularly on public climate financing mechanisms. The types of climate finance available vary from grants and concessional loans, to guarantees and private equity. The architecture has differing structures of governance, modalities and objectives. The proliferation of climate finance mechanisms increases the challenges of coordinating and accessing finance, as well as its monitoring. While the transparency of climate finance programmed through multilateral initiatives is increasing, detailed information on bilateral initiatives, regional and national funds are often less readily available.
The climate finance architecture
Click on the image for larger version.
Implementing Agencies and Institutions
- AfDB – African Development Bank
- AFD – Agence Française de Développement (French Development Agency)
- ADB – Asian Development Bank
- BEIS – Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy
- BMZ – Bundeministerium für Wirtschaftliche Zusammenarbeit und Entwicklung (federal ministry of economic cooperation and development, Germany)
- CIDA – Canadian International Development Agency
- DEFRA – Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (UK)
- DFAT – Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (Australia)
- DFC – United States International Development Finance Corporation
- EBRD – European Bank for Reconstruction and Development
- EIB – European Investment Bank
- Ex-Im – Export-Import Bank of the United States
- FAO – Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations
- FFEM – Fonds Français pour l’Environnement Mondial (French global environment facility)
- GIZ – Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit GmbH (German technical cooperation)
- IDB – Inter-American Development Bank
- IFAD – International Fund for Agricultural Development
- JBIC – Japan Bank of International Cooperation
- JICA – Japan International Cooperation Agency
- KfW – Kreditanstalt für Wiederaufbau (German development bank)
- MIES – Mission Interministérielle de l’Effet de Serre (inter-ministerial taskforce on climate change, France)
- MOFA – Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Japan)
- NMFA – Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Norway)
- NORAD – Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation
- UNDP – United Nations Development Programme
- UNEP – United Nations Environment Programme
- USAID – US Agency for International Development
- WB – World Bank
Multilateral Funds and Initiatives
- ACT – Accelerating Coal Transition program (implemented through WB, ADB, AfDB, EBRD and IDB)
- AF – Adaptation Fund (GEF acts as secretariat and WB as trustee)
- ACCF – Africa Climate Change Fund
- AREI – African Renewable Energy Initiative
- ASAP – Adaptation for Smallholder Agriculture Programme
- CAFI – Central African Forest Initiative
- CBFF – Congo Basin Forest Fund (hosted by AfDB)
- CDM – Clean Development Mechanism (implemented under the Kyoto Protocol)
- CIF – Climate Investment Funds (implemented through WB, ADB, AfDB, EBRD, and IDB)
- CTF – Clean Technology Fund (implemented through WB, ADB, AfDB, EBRD, and IDB)
- FCPF – Forest Carbon Partnership Facility
- FIP – Forest Investment Program (implemented through WB, ADB, AfDB, EBRD, and IDB)
- GCCA – Global Climate Change Alliance
- GCF – Green Climate Fund
- GEF – Global Environment Facility
- GEEREF – Global Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Fund (hosted by EIB)
- JI – Joint Implementation (implemented under the Kyoto Protocol)
- LDCF – Least Developed Countries Fund (hosted by the GEF)
- PMR – Partnership for Market Readiness
- PPCR – Pilot Program on Climate Resilience (implemented through World Bank, ADB, AfDB, EBRD, and IDB)
- SCCF – Special Climate Change Fund (hosted by the GEF)
- SCF – Strategic Climate Fund (implemented through WB, ADB, AfDB, EBRD, and IDB)
- SREP – Scaling Up Renewable Energy Program for Low Income Countries (implemented through WB, ADB, AfDB, EBRD, and IDB)
- UN-REDD – United Nations Collaborative Programme on Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation
National, Regional, and Country-Collaborative Funds
- Amazon Fund
- Bangladesh Climate Change Resilience Fund
- Bangladesh Climate Change Trust Fund
- Benin National Fund for the Environment and Climate
- Brazilian National Fund on Climate Change
- Cambodia Climate Change Alliance Trust Fund
- Climate Resilient Green Economy—Ethiopia
- CVF and V20 Joint Multi Donor Fund
- Guyana REDD+ Investment Fund
- Indonesia Climate Change Trust Fund
- Just Energy Transition Partnerships (JETPs; South Africa, Indonesia, Vietnam)
- Maldives Climate Change Trust Fund
- Mali Climate Fund
- Mexico Climate Change Fund
- Philippines People’s Survival Fund
- Rwanda’s Green Fund
- South Africa Green Fund
Bilateral Funds and Initiatives
- GCCI – Global Climate Change Initiative (US)
- GCPF – Global Climate Partnership Fund (Germany, UK and Denmark)
- ICF – International Climate Fund (UK)
- IKI – Internationale Klimaschutzinitiative (international climate initiative, Germany)
- MDG-F – MDG Achievement Fund (implemented by UNDP)
- NAMA Facility – Nationally Appropriate Mitigation Action facility (UK, Germany, Denmark and the EC)
- NICFI – Norway’s International Climate Forest Initiative
- REM – REDD+ Early Movers (Germany and UK)